Image Encryption Using P-Fibonacci Decomposition and Transform
Introduction
This paper has introduced a new image encryption algorithm, which use one of Truncated P-Fibonacci Bit-planes (TPFB) of another source image as the security key image. The user has the flexibility to use any new or existing image as a source image to generate the TPFBs and to include any scrambling algorithm into our proposed encryption algorithm. The experimental results have shown that the proposed algorithm has excellent performance for image encryption. It has a sufficiently large key space, ensuring a high security level. It has potential applications in privacy and copyright protection.
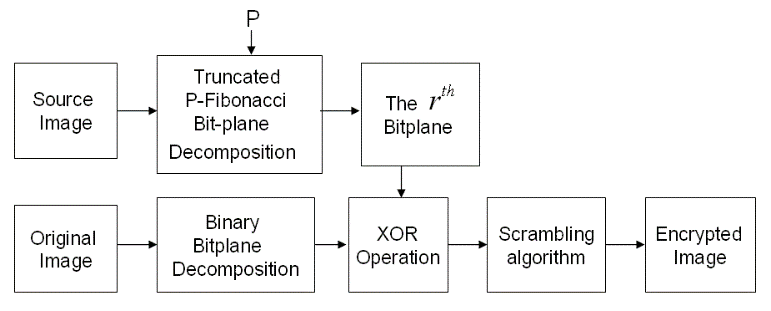 |
Main results
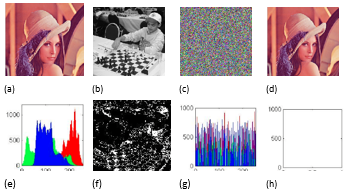 |
| Figure 1. Color image encryption. (a) The original color image with the size of 256×256; (b) The source image with the size of 256×256; (c) The encrypted color image; (d) The recovered image; (e) Histogram of the original image in (a); (f) the TPFB of the source image in (b), p=2; (g) Histogram of the encrypted image in (c); (h) Histogram of the difference between (a) and (d). |
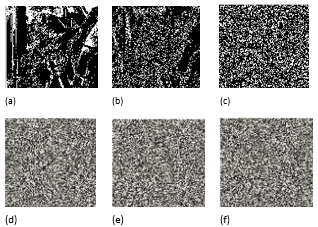 |
| Figure 2. Image encrypted using different TPFBs of a source image in Figure 3(b) with p=3. (a) The TPFB; (b) The TPFB; (c) The TPFB; (d)The encrypted image using the bit-plane in (a); (e) The encrypted image using the bit-plane in (b); (f) The encrypted image using the bit-plane in (c). |
 |
| Figure 3. The encrypted results using the TPFBs with different p values (a) The TPFB, p=3; (b) The TPFB, p=5; (c) The TPFB, p=7; (d) The encrypted image using (a); (e) The encrypted image using (b); (f) The encrypted image using (c). |